Targeted Therapy Liver Cancer: What You Need to Know
When talking about Targeted Therapy for Liver Cancer, a treatment approach that attacks cancer cells by focusing on specific molecular pathways rather than using broad‑spectrum chemotherapy. Also known as targeted liver cancer treatment, it sits at the core of modern Precision Medicine, which tailors care to each patient’s genetic profile. This strategy reshapes how doctors manage hepatocellular carcinoma, turning once‑generic regimens into personalized plans that aim for higher efficacy and fewer side effects. The rise of targeted therapy liver cancer has sparked a wave of clinical trials, insurance updates, and patient‑education resources you’ll see reflected across our article collection.
Key Drugs That Define the Landscape
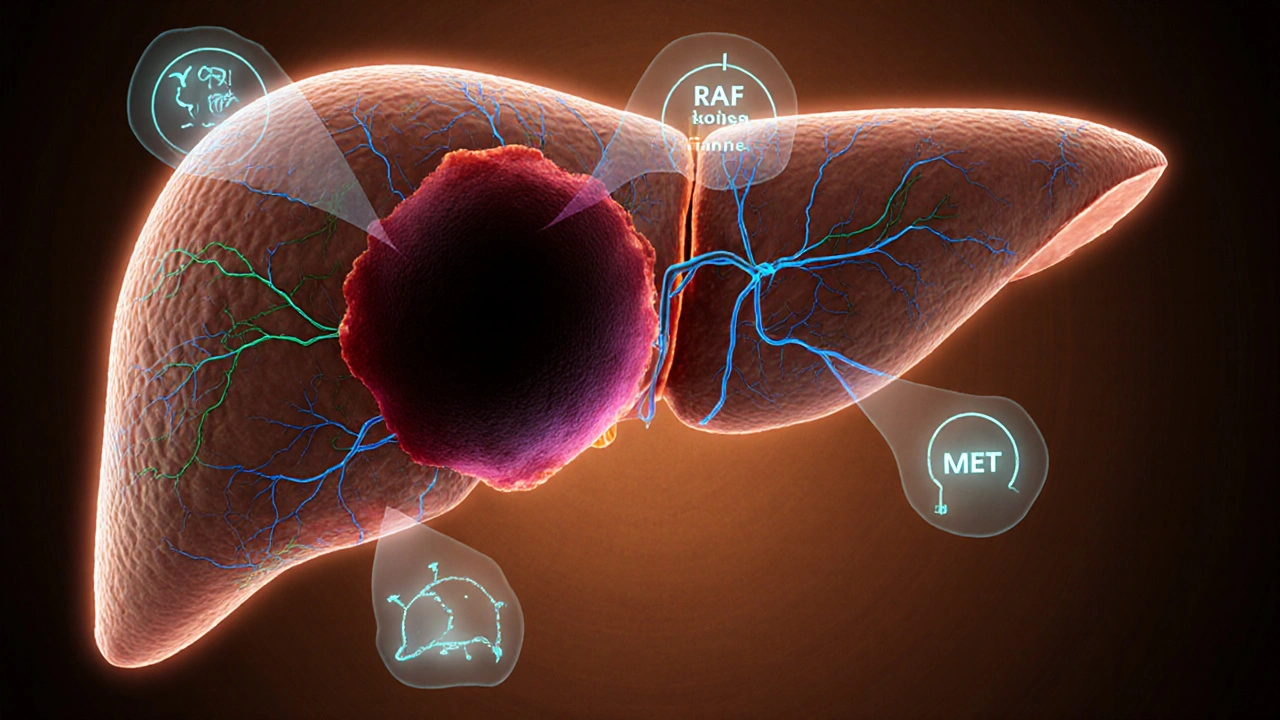
One of the first breakthroughs was Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that blocks RAF, VEGFR, and PDGFR pathways. Its main attribute is the ability to halt tumor angiogenesis, and the value it delivers is a measurable extension of overall survival—often six months longer than best‑supportive care alone. Another heavyweight, Lenvatinib, shares a similar target profile but adds FGFR inhibition, giving patients an alternative when sorafenib isn’t tolerated. Both drugs encapsulate the principle that targeted therapy for liver cancer works by interrupting the signals cancer cells need to grow, a classic example of a Subject‑Predicate‑Object triple: "Targeted therapy for liver cancer interrupts angiogenic signaling." Real‑world usage data shows that dose adjustments based on liver function tests are crucial, and side‑effect management—hand‑foot skin reaction, hypertension, and fatigue—plays a big role in keeping patients on therapy.
Beyond the drugs themselves, the success of these treatments relies heavily on Molecular Biomarkers. Biomarkers such as AFP levels, TP53 mutations, and CTNNB1 alterations serve as attributes that help clinicians decide who is likely to benefit. When a patient’s tumor shows high VEGF expression, the value is a higher probability of responding to sorafenib; when FGFR2 fusions appear, lenvatinib becomes a stronger candidate. This link creates another semantic triple: "Molecular biomarkers guide targeted therapy decisions." The testing process—often a next‑generation sequencing panel—requires a biopsy, a lab with CLIA certification, and a clear communication channel between oncologist and pathologist. The result is a treatment roadmap that feels less like guesswork and more like a precision‑engineered plan.
While targeted agents dominate the scene, Immunotherapy is emerging as a complementary force. Checkpoint inhibitors such as atezolizumab, when combined with bevacizumab, have shown survival benefits that rival traditional targeted drugs. This demonstrates the triple: "Immunotherapy enhances the effectiveness of targeted therapy for liver cancer." The combination leverages both the immune system’s ability to recognize tumor antigens and the anti‑angiogenic effects of VEGF blockade, providing a two‑pronged attack. As new trials explore triples of targeted drug + immunotherapy + biomarker‑driven selection, the field moves toward a truly integrated approach.
Looking ahead, you’ll find a mix of practical guides and deep‑dive analyses in the posts below. Some articles walk you through how to evaluate drug‑interaction warnings when buying generic versions of sorafenib or lenvatinib, while others compare side‑effect profiles and cost‑saving tips. We also cover the psychological impact of a liver cancer diagnosis and how targeted therapy fits into broader wellness plans. All of this aims to give you a clear picture of where targeted therapy liver cancer stands today, what tools are available, and how you can make informed decisions with your care team. Dive in to see the full range of resources we’ve gathered for you.
Targeted Therapy for Liver Cancer: Latest Treatments and What They Mean
Explore the latest targeted therapies for liver cancer, how they work, approved options, selection criteria, side‑effect management, and upcoming treatment trends.
Read More