Hatch-Waxman Act: How It Shaped Generic Drugs and Drug Prices
When you pick up a generic pill at the pharmacy, you’re benefiting from a law passed in 1984 called the Hatch-Waxman Act, a U.S. law that created a legal pathway for generic drugs to reach the market without repeating costly clinical trials. Also known as the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act, it’s the reason you can buy metformin or lisinopril for a few dollars instead of hundreds.
This law didn’t just make generics possible—it rewrote the rules between brand-name drugmakers and companies that copy them. Before Hatch-Waxman, a generic maker had to prove a drug was safe and effective all over again, even if the original brand had already done so. That made generics too expensive to produce. The Act let generic companies file an Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA), using the brand’s data to prove equivalence. But it also gave brand-name companies up to five extra years of market exclusivity if they did new studies for pediatric use or other improvements. This balance kept innovation alive while opening the door to competition.
The Act also created a system for patent challenges. If a generic company believes a brand’s patent is invalid or not being infringed, they can file a certification saying so. This triggered the first wave of generic competition for blockbuster drugs like Lipitor and Nexium. It’s why you see so many drug lawsuits today—pharmaceutical companies fight to extend patents, while generics push to enter early. The result? Lower prices for millions. But it’s not perfect. Some companies game the system with "pay-for-delay" deals, where brand makers pay generics to delay entry. The FTC has fought these, but they still happen.
What you’ll find in the articles below isn’t just about patents and paperwork. It’s about real-world impact: how Hatch-Waxman made it possible for pharmacies to profit from generics, why some people react differently to generic versions of levothyroxine or warfarin, and how pediatric exclusivity—another part of this law—gives companies extra market time to study drugs for kids. You’ll see how this law connects to everything from insurance coverage for counterfeit drugs to the rise of statin intolerance clinics. It’s the hidden engine behind your prescription costs, your medication choices, and even the way doctors manage complex regimens. This isn’t history—it’s the framework that still shapes your health today.
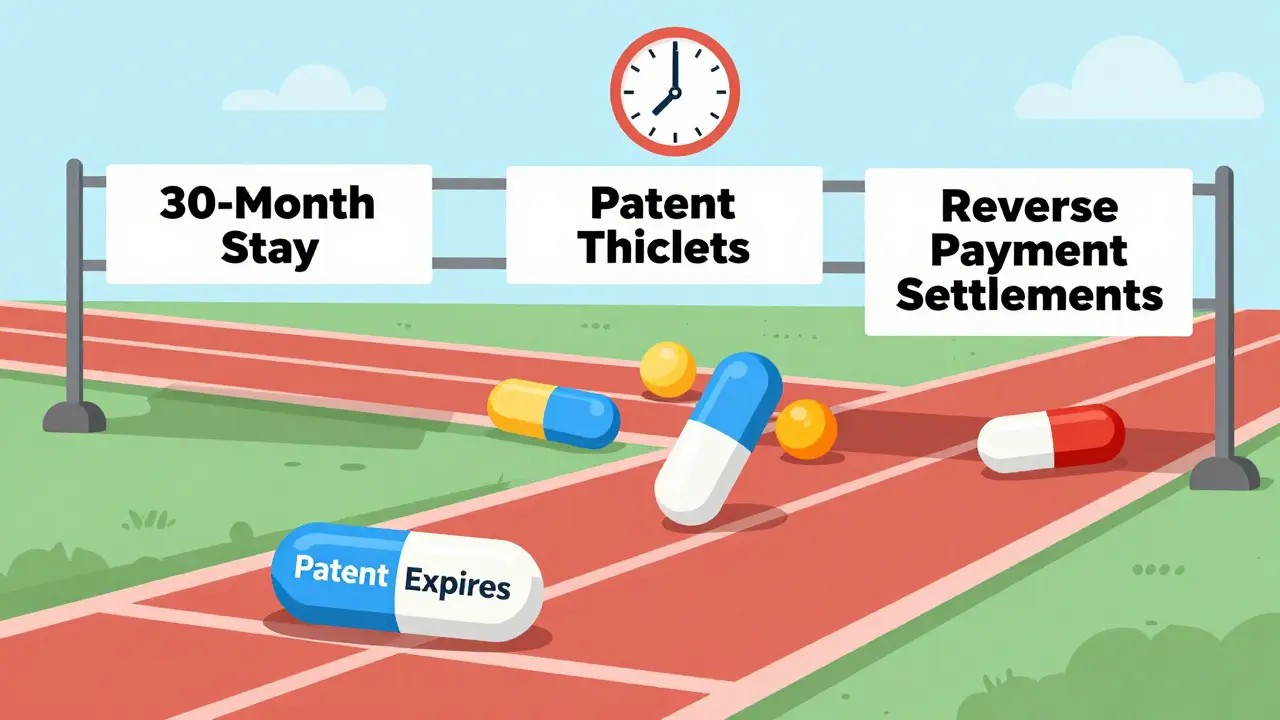
Generic Drug Availability: From Patent Expiration to Market Launch
Generic drugs don't launch right after patents expire. Legal delays, patent thickets, and corporate tactics create years-long gaps between expiration and availability - costing patients billions. Here's how it really works.
Read More
First Generic Approval: Why It Matters and What It Means for Drug Prices and Access
First generic approval by the FDA gives a company 180 days of exclusive rights to sell the cheapest version of a brand-name drug. This system drives down prices, saves billions, and improves patient access - but it's not without challenges.
Read More
Patent Term Restoration (PTE): How Drug Patents Get Extra Time
Patent Term Restoration gives drug makers extra patent time to make up for FDA approval delays. Learn how it works, who benefits, and why it keeps drug prices high.
Read More