FDA Approved Liver Drugs: What You Need to Know
When talking about FDA approved liver drugs, medications that have passed the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's rigorous safety and efficacy standards for treating liver conditions. Also known as FDA‑cleared hepatology medicines, they include antivirals for hepatitis, anti‑fibrotic agents for cirrhosis, and cholesterol‑lowering drugs that protect liver tissue. Understanding these drugs starts with three key ideas: the FDA approval process, the impact of clinical trials and safety reviews, the prevalence of generic medications, and how they intersect with liver disease, the condition they aim to manage.
Why the FDA approval process matters for liver therapy
Every liver drug listed here has cleared the FDA’s multi‑step review, which means the drug showed measurable benefit in reducing viral load, slowing fibrosis, or improving liver enzyme levels during controlled trials. The process also checks for drug‑drug interactions—a crucial factor because many patients with liver disease are already on blood thinners, statins, or diabetes meds. For example, a generic version of a hepatitis C antiviral might be cheaper, but you still need to confirm it doesn’t clash with your existing regimen. This is where the concept of drug interactions becomes a practical checkpoint before you pick a therapy.
Speaking of cost, generic medications play a huge role in making liver care affordable. The posts below show how buying cheap generic options online—whether it's a low‑cost version of a statin, a diuretic like Lasix, or an anti‑inflammatory like Celebrex—can save you money while still delivering the same therapeutic effect. When a brand‑name liver drug goes off‑patent, the generic version inherits the same FDA approval, meaning you get the same safety profile without the premium price tag. That’s why many of our guides focus on spotting legit online pharmacies, comparing pricing, and understanding dosing.
But affordability isn’t the only piece of the puzzle. Liver disease comes in many flavors—viral hepatitis, non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcoholic cirrhosis, and genetic disorders like hemochromatosis. Each condition calls for a specific drug class. Antivirals target viral replication, while agents like ursodeoxycholic acid help with bile flow in cholestatic disease. Knowing which FDA approved drug aligns with your diagnosis helps you avoid trial‑and‑error prescribing. The collection of articles on this page walks you through comparisons (like brand versus generic), safety tips, and real‑world pricing insights so you can match the right drug to your health needs.
Now that you’ve got the basics—how the FDA clears liver drugs, why generics matter, and the importance of checking interactions—take a look at the resources below. You’ll find side‑by‑side comparisons, buying guides, and condition‑specific advice that turn this overview into actionable steps for managing your liver health.
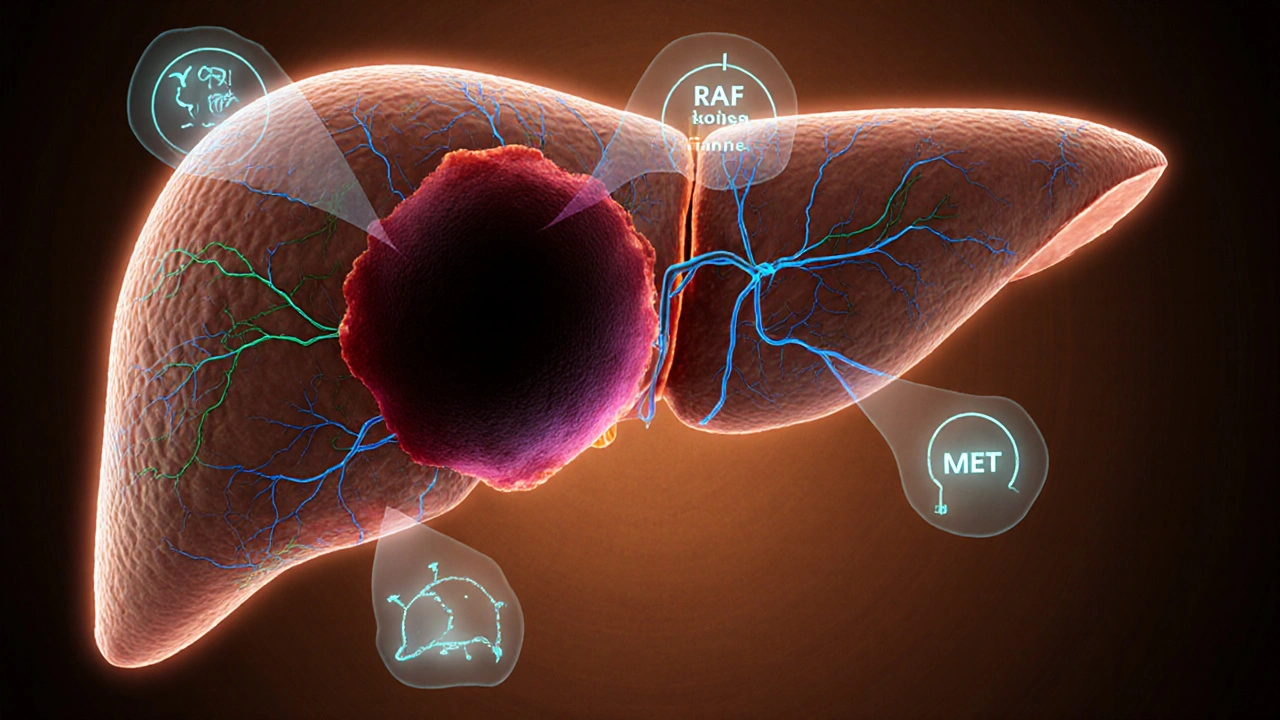
Targeted Therapy for Liver Cancer: Latest Treatments and What They Mean
Explore the latest targeted therapies for liver cancer, how they work, approved options, selection criteria, side‑effect management, and upcoming treatment trends.
Read More