Pharmaceutical Supply Chain: How Drugs Get from Factory to Your Pharmacy
When you pick up a prescription, you might think the drug just appeared on the shelf. But behind that pill is a complex pharmaceutical supply chain, the network of manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, and middlemen that moves medicines from labs to patients. Also known as drug distribution system, it’s where pricing, access, and even availability are decided—not just by doctors, but by profit margins and corporate contracts.
This system isn’t just about moving boxes. It’s shaped by generic drugs, low-cost versions of brand-name medicines that make up 90% of prescriptions but only 25% of spending. These generics drive pharmacy profits, yet many independent pharmacies are closing because they get squeezed by PBM reimbursement, the payments pharmacies receive from pharmacy benefit managers who control which drugs get covered and at what price. Meanwhile, patent extensions and regulatory loopholes—like patent term restoration, a rule that lets drugmakers extend exclusivity to make up for FDA delays—keep prices high even after generics are ready to launch.
What does this mean for you? Your medication might be cheaper because of generics, but the pharmacy filling it could be losing money. Your insurance might cover a drug because a PBM pushed it, not because it’s the best option. And if a factory shuts down or a shipment gets delayed, you could face a shortage—even if the drug is widely used. The system is built for efficiency, not transparency, and most patients never see the gears turning.
That’s why the articles here dig into the real mechanics: how pharmacy margins work, why some generics cause unexpected side effects, how drug patents get extended, and what happens when a single manufacturer controls a life-saving medicine. You’ll find real stories about how supply chain gaps affect cancer survivors, how pediatric exclusivity blocks cheaper options for kids, and why your statin might cost more than you think—even if it’s "generic." This isn’t theory. It’s what’s happening in warehouses, billing systems, and your medicine cabinet right now.
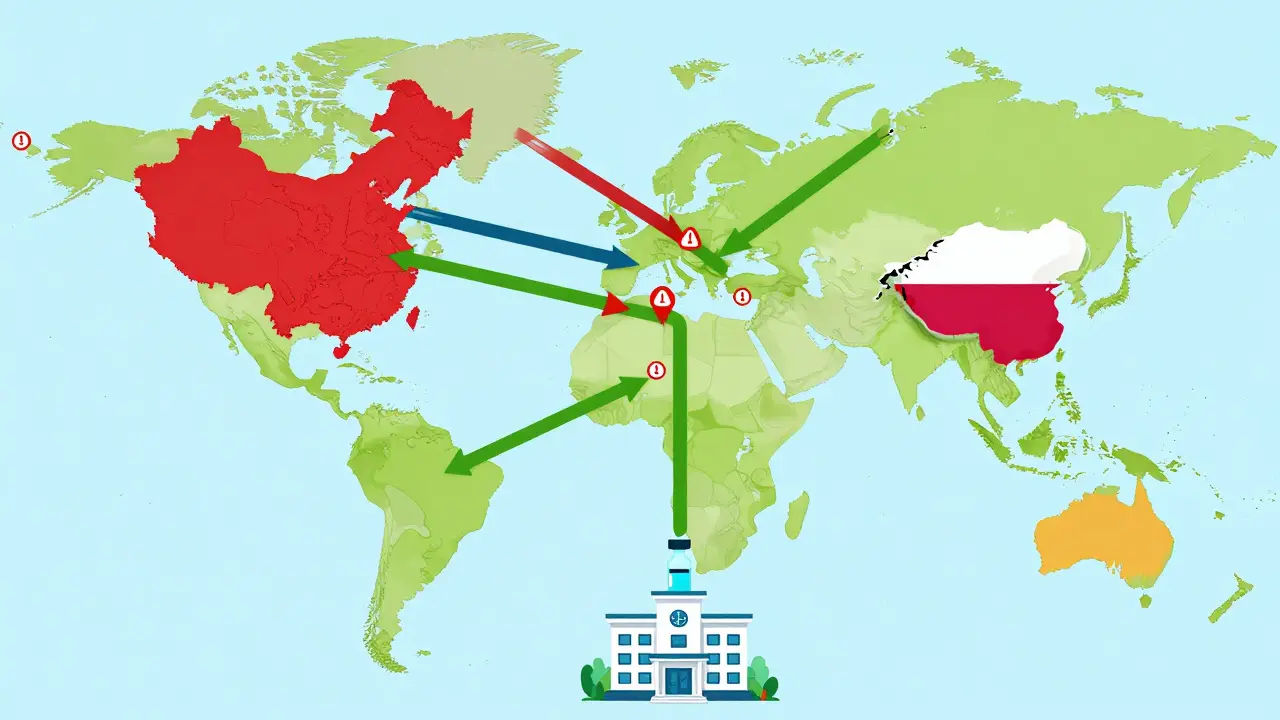
Preventive Measures for Building Resilient Pharmaceutical Supply Chains
Pharmaceutical supply chains are under strain, causing dangerous drug shortages. Learn how diversifying suppliers, using AI, building buffer stock, and modernizing manufacturing can create resilient systems that keep life-saving medicines available.
Read More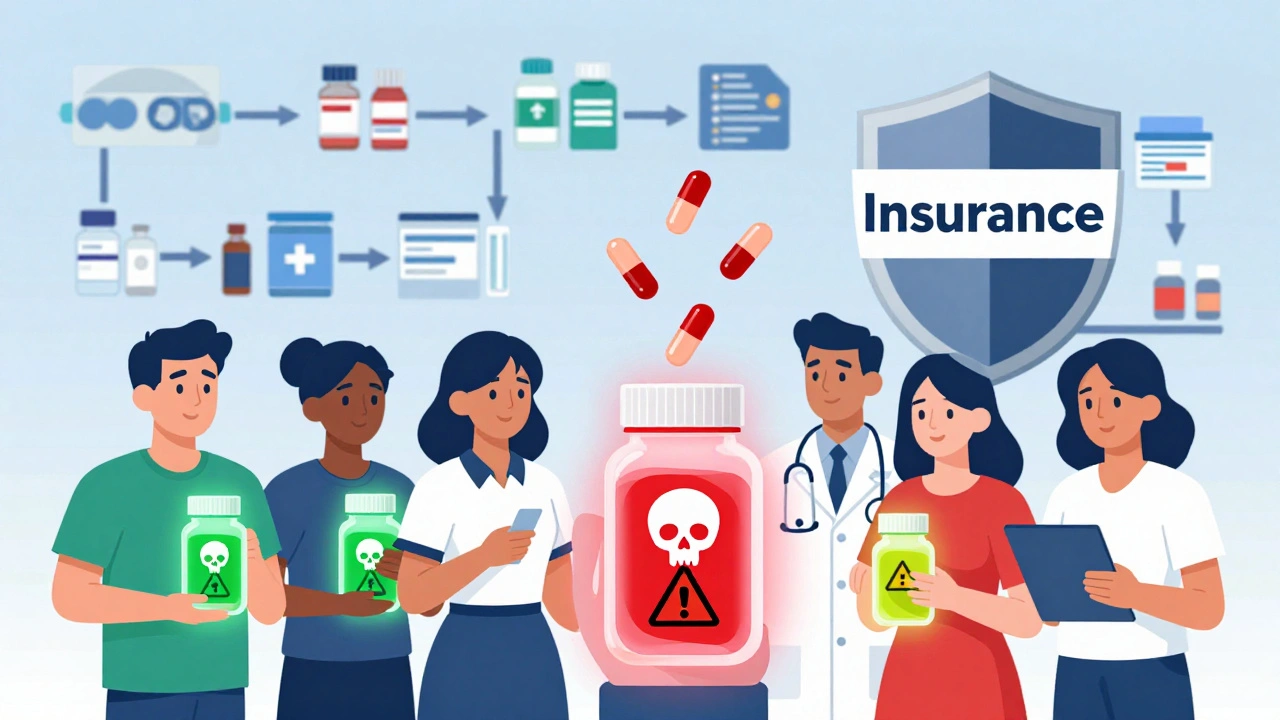
Insurance Protections and Coverage for Counterfeit Drug Risks
Counterfeit drugs threaten patient safety and cost the global economy $200 billion annually. Insurance can protect businesses that unknowingly distribute fake medicines - but only if they follow strict supply chain practices.
Read More