Dopamine Interaction: What You Need to Know About Drugs, Supplements, and Brain Chemistry
When you hear dopamine interaction, the way certain substances change how dopamine works in your brain. Also known as neurotransmitter interference, it’s not just about feeling good—it’s about safety, side effects, and whether your meds are working as they should. Dopamine isn’t just the "feel-good" chemical. It’s your brain’s control center for motivation, movement, focus, and even how you respond to pain. When something—like a pill, supplement, or even alcohol—messes with dopamine levels or how it binds to receptors, the effects can be subtle or serious.
Take bupropion, an antidepressant and smoking cessation aid that boosts dopamine levels. It’s designed to help you quit smoking by increasing dopamine, but if you’re also taking other drugs that affect dopamine—like certain ADHD meds or MAO inhibitors—you could be risking seizures or dangerously high blood pressure. That’s a real dopamine interaction, not just a warning on a label. Same goes for herbal supplements, like St. John’s wort or Jamaican Dogwood. People think "natural" means safe, but some herbs block dopamine reuptake or alter enzyme activity, which can clash with antidepressants, Parkinson’s drugs, or even birth control. You might not feel anything right away, but over time, your brain gets out of sync.
Dopamine interaction doesn’t just happen with pills and herbs. Even something as simple as caffeine can play a role—especially if you’re on a medication that slows down how your liver breaks it down. And if you’re taking statins or blood thinners, your liver is already busy. Add in a supplement that changes dopamine metabolism, and you’re stacking risks you didn’t even know about. That’s why doctors ask for a full list of everything you take, not just prescriptions. The dopamine interaction you ignore today could lead to fatigue, anxiety, tremors, or worse down the line.
What you’ll find below isn’t a list of every drug that touches dopamine. It’s a real-world collection of cases where people got caught off guard—by supplements they thought were harmless, by combinations they didn’t realize were risky, or by side effects they blamed on aging instead of chemistry. These aren’t theory pieces. They’re stories from people who had to learn the hard way. And if you’re on any kind of long-term medication, or you take supplements to help with sleep, mood, or energy, you need to know what’s really going on inside your brain.
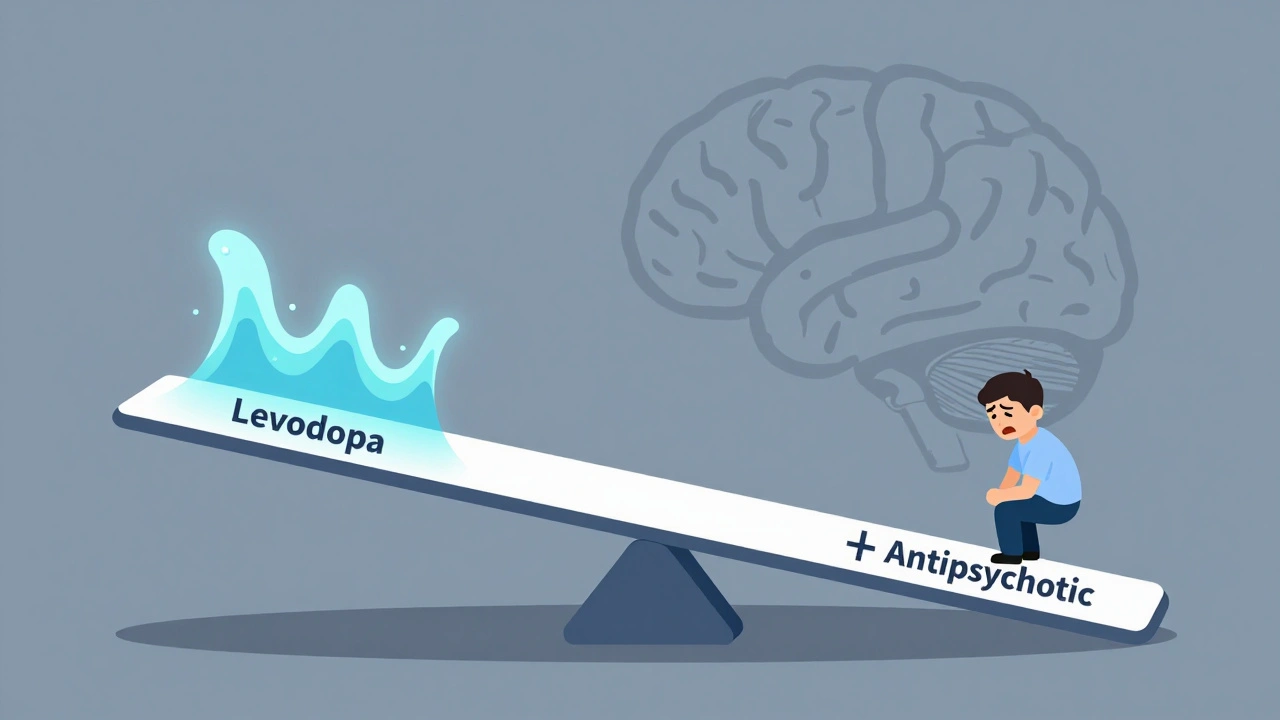
Levodopa and Antipsychotics: How Opposing Dopamine Effects Worsen Symptoms
Levodopa and antipsychotics have opposing effects on dopamine, making it dangerous to use them together. This article explains how this interaction worsens symptoms in Parkinson’s and schizophrenia, and what newer treatments are doing to solve it.
Read More